Franklin County Courthouse (1887–1974)
| Franklin County Courthouse | |
|---|---|
 The courthouse c. 1900–10 | |
 Present-day site of the building | |
| General information | |
| Address | 380 S. High St., Columbus, Ohio[1] |
| Coordinates | 39°57′16″N 82°59′54″W / 39.954508°N 82.998458°W |
| Construction started | July 4, 1885 |
| Opening | July 13, 1887 |
| Demolished | 1974 |
| Cost | $470,000 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | George H. Maetzel |
| Main contractor | George Bellows Sr.[2] |
The 1887 Franklin County Courthouse was the second permanent courthouse of Franklin County, Ohio. The building, located in the county seat of Columbus, stood from 1887 to 1974. It replaced a smaller courthouse on the site, extant from 1840 to c. 1884. The 1887 courthouse deteriorated over several decades, and the site was eventually replaced with Dorrian Commons Park, open from 1976 to 2018; the court moved to a new building nearby. As of 2020, the site is planned to once again hold the county's Municipal Court building.
History
[edit]Prior spaces
[edit]

The first spaces for the court was in rented rooms, and the first county building was a log jail ordered built in 1804; it is not known whether the building housed records. The first courthouse was built 1807-08 in Franklinton (then the county seat); its awarded builder was Lucas Sullivant, also first clerk of the court and founder of Franklinton. After the county government moved to Columbus in 1824, the court moved to the U.S. District Court Building on the northwest corner of Capitol Square. In 1828 or 1829, after the space was found inadequate, a long single-story office building was built to the rear of the court building; these buildings held the county court until 1840.[3][4]
With the growth of Columbus and settlement of its adjacent areas, county business increased, prompting discussion of a permanent courthouse. In 1837, a site was donated to the county at Mound and High Streets, so long as a courthouse was built there. The first permanent courthouse was then built, and completed in 1840. The two-story brick and stone building cost $41,000. An annex was built to its south in 1853. A jail was added to the complex in 1865, along with other expansions around the same time.[3]
A fire destroyed many records in this courthouse in 1879, prompting discussion of a new courthouse building.[5]
Planning and construction
[edit]
A $500,000 bond issue vote taken in 1884[6] prompted the construction of a new courthouse and jail. George H. Maetzel was the appointed architect. Plans began to demolish the existing structures on the site, and space was rented for office and court space, while a temporary building was constructed to hold the county records. The judge of the court of common pleas appointed a building commission in April 1884 to work on the courthouse plans. The commission visited other cities to learn about architecture, interior space uses, and project costs. The building's cornerstone was laid on July 4, 1885, accompanying a parade and celebration.[7] The building was dedicated on July 13, 1887, on the hundredth anniversary of the passage of the Northwest Ordinance. It had a cost of $470,000.[4] At the time of its opening, and for years thereafter, the building was considered only second to the Ohio Statehouse in grandeur.[3]
Demise and replacement
[edit]
By 1937, the interior had been remodeled, ruining much of the building's original ornate interior. Skylights were covered and mezzanines reconstructed into wholly separate floors. Working space became limited, prompting thousands of the county's older documents and volumes to be moved to the building's attic, which experienced roof leaks, insecure floors, poor organization, and poor lighting and ventilation. The space was reported as a fire hazard at risk to loss of the entire building.[3]
An annex was built to the building's south in 1953 (now known as the Karnes Building).[8] The statue of Justice was removed in 1953. A roof leak in 1954 prompted an engineering inspection, which found serious deterioration in the clocktower.[9] Also at this time, pieces of debris began falling to the sidewalk, including portions from the clocktower.[8]
In 1954, the building's clocktower was removed, and around this time other parts of the roofing were removed and replaced with simpler elements.[6] In 1966, county commissioners assessed the cost of a new courthouse and jail, which would save $5.5 million over maintaining and renovating the then-current building.[10] Two tax levies were put on ballots to replace the courthouse, though only one passed. Another was approved in 1971. The new Hall of Justice was completed in 1952 as the first of several structures replacing functions of the courthouse.[8]
By late 1974, with demolition imminent, all county functions had moved over to the new Hall of Justice and the courthouse annex. An over-200-person auction was held over multiple days in August 1974. The auction sold off items from all floors of the building, and left items around the building, including crime scene photos scattered on the floors, autopsy negatives, and cabinets full of murder and burglary records. Sale items included office chairs, the High Street exterior doors, and the woodwork and doors for the building's vestibule.[11]
The building was razed in September 1974, 90 years to the month from the demolition of the courthouse before it.[6] A common pleas court judge refused to issue an order to delay demolition in August, as a group wanted to study alternatives to demolition.[12]
The site was replaced with Dorrian Commons Park, open from 1976 to 2018; the courthouse moved to a new building nearby, in the Franklin County Government Center. In 2020, The Columbus Dispatch reported that the site is now planned to once again hold the county's courthouse.[13]

The 1887 courthouse's cornerstone and several of its entranceway columns are located at the James A. Karnes Building.[14] The cornerstone was stored in a garage near Dorrian (then Franklin) Commons Park rescued from a garbage dump in 1977, after having been accidentally carted off.[15] In 1979, it was utilized as a planter by the county's horticulturalist, who fit five plants' roots into the hole that formerly held a copper box time capsule.[16] The cornerstone, first opened in October 1974, held a 15-pound copper box containing newspapers, government reports, and a city directory.[17]
Attributes
[edit]The courthouse had no specific architectural style, with a combination of features from various styles, predominantly French Renaissance style. The building closely resembled the Allen County Courthouse in Lima and the Madison County Courthouse in London, both also designed by George H. Maetzel. The building received acclaim from the public and press at its opening.[3]
The building was made of Berea Sandstone. It had entrances flanked by large red granite pillars. The High Street entrance featured the Great Seal of Ohio between two allegorical female figures as a sculptural group atop the entranceway pediment. The building was topped with an ornate clocktower and belfry, itself topped with a cupola and statue of "Justice". The belfry housed the 1840 courthouse's bell, which weighed 1,000 lbs.[3] The roofline consisted of three sections of Mansard roofs – one in the center below the clocktower and two on either end of the building.[8]
The courthouse clock was wound each week. It sat in a loft below the belfry, and had parts designed by E. Howard. The four-faced clock had run continuously since 1887, though by the time it was removed, only two of the four faces were accurate.[9]
-
Early recolored postcard of the courthouse
-
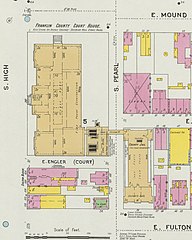
1901 map of the courthouse and Franklin County Jail
-
The replacement Franklin County Municipal Court (built 1979), Courthouse (1991) and Hall of Justice (1973)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ National Register of Historic Places Registration: Franklin Park Conservatory. File Unit: National Register of Historic Places and National Historic Landmarks Program Records: Ohio, 1964 - 2013. National Park Service. Retrieved January 15, 2021.
- ^ Darbee, Jeff. "City Quotient: Columbus Architect George Bellows". Columbus Monthly.
- ^ a b c d e f (Ohio), Historical Records Survey (2006-04-12). "Inventory of the County Archives of Ohio - Historical Records Survey (Ohio) - Google Books". Retrieved 2021-02-11.
- ^ a b Samuelson, Robert E.; et al. (Pasquale C. Grado, Judith L. Kitchen, Jeffrey T. Darbee) (1976). Architecture: Columbus. The Foundation of The Columbus Chapter of The American Institute of Architects. p. 216. OCLC 2697928.
- ^ "Highlights of Columbus History". The Columbus Dispatch. October 14, 1962. pp. 154–156. Retrieved October 23, 2021.
- ^ a b c "The Franklin County Courthouse". The Columbus Dispatch. April 6, 1980. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "Independence Day". The Columbus Dispatch. July 3, 1885. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ a b c d "Courthouse is New and So Is the Name". The Columbus Dispatch. February 18, 1979. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ a b "Clock Watcher Remembers Good Times". The Columbus Dispatch. November 3, 1974. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "New Courthouse Advantage Cited". The Columbus Dispatch. October 9, 1966. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "Courthouse Going, Going..." The Columbus Dispatch. August 29, 1974. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "Courthouse Order Denied". The Columbus Dispatch. August 2, 1974. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ Futty, John. "New Municipal Courthouse to replace Downtown park at South High and Mound streets". The Columbus Dispatch. Archived from the original on 2020-03-29. Retrieved 2021-01-05.
- ^ Darbee, Jeffrey T.; Recchie, Nancy A. (2008). The AIA Guide to Columbus. Ohio University Press. p. 57. ISBN 9780821416846.
- ^ "Courthouse Cornerstone is Recovered From Dump". The Columbus Dispatch. October 21, 1977. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "Cornerstone Gets New Duty". The Columbus Dispatch. July 22, 1979. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
- ^ "Lid Comes Off Cornerstone". The Columbus Dispatch. October 17, 1974. Retrieved 2022-08-29.
External links
[edit] Media related to 1887 Franklin County Courthouse (Ohio) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1887 Franklin County Courthouse (Ohio) at Wikimedia Commons